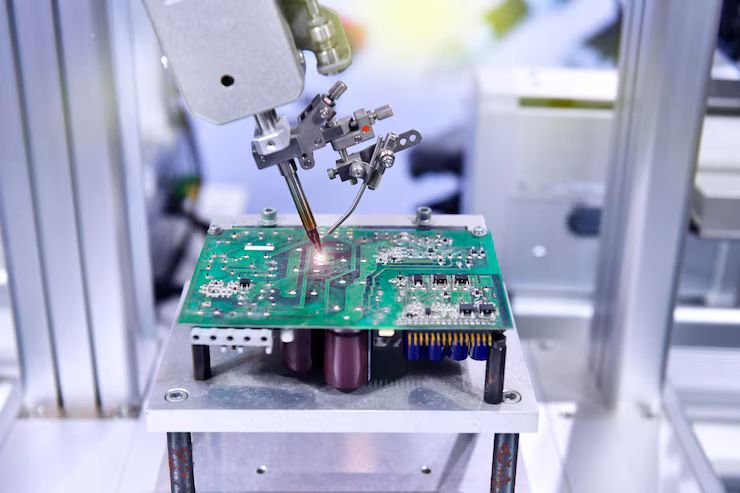
Electronic assembly machinery refers to specialized equipment used to assemble electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs) and related substrates. These machines exist to support accurate, repeatable, and scalable production of electronic devices that are used in everyday life, from consumer electronics to industrial control systems.
At the core of electronics manufacturing is the need to place tiny components—such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits—onto PCBs with high precision. Manual assembly cannot consistently achieve the speed and accuracy required for modern electronics. Electronic assembly machinery addresses this challenge by automating placement, soldering, and inspection processes.
The development of this machinery evolved alongside miniaturization in electronics. As components became smaller and circuit density increased, automated systems became essential. Today, electronic assembly machinery forms the physical backbone of electronics manufacturing, translating digital designs into functional hardware.
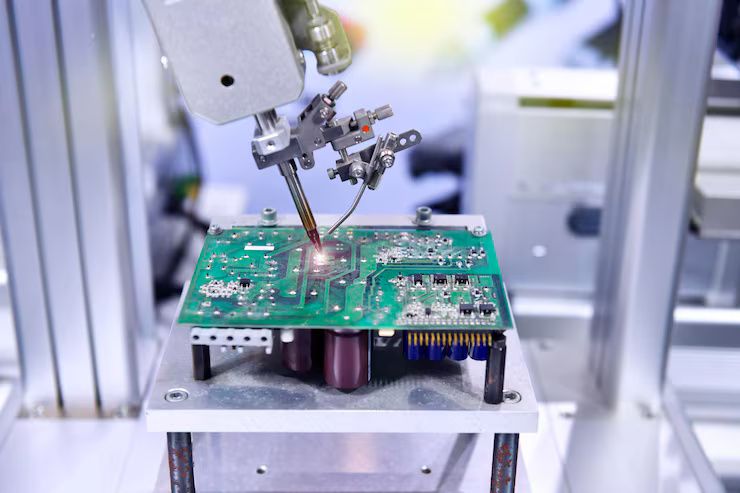
Importance: Why Electronic Assembly Machinery Matters Today
Electronic assembly machinery is critical because electronics are deeply embedded in modern infrastructure, communication, healthcare, transportation, and energy systems. The reliability and performance of these systems depend heavily on how accurately electronic components are assembled.
Key reasons this topic matters today include:
-
Support for high-volume production
Automated assembly enables consistent output at industrial scale. -
Precision and repeatability
Machines ensure uniform placement and soldering across thousands of circuit boards. -
Compatibility with miniaturized components
Advanced machinery handles fine-pitch and surface-mount components. -
Quality and reliability
Integrated inspection systems help detect defects early in the manufacturing process. -
Foundation for industrial automation
Electronic assembly machinery integrates with digital manufacturing and smart factory systems.
As global demand for electronics continues to grow, the role of efficient and accurate assembly machinery becomes increasingly significant across supply chains.
Recent Updates: Trends and Developments in the Past Year
In the past year, electronic assembly machinery has seen steady progress driven by automation, data integration, and efficiency improvements.
Key developments observed during 2025 include:
-
Advanced SMT assembly integration (2025)
Surface-mount technology lines increasingly combine placement, soldering, and inspection into synchronized workflows. -
Artificial intelligence in inspection systems
Automated optical inspection (AOI) tools began using enhanced pattern recognition to identify subtle assembly variations. -
Flexible production lines
Machinery designs now support faster changeovers to accommodate varied PCB designs. -
Energy-efficient equipment designs
Manufacturers focused on reducing power consumption in reflow ovens and auxiliary systems. -
Data connectivity and traceability
Assembly machines increasingly record process data to support quality analysis and compliance tracking.
These updates reflect a shift toward smarter, more adaptable electronics manufacturing environments.
Laws or Policies Influencing Electronics Manufacturing in India
In India, electronics manufacturing and the use of electronic assembly machinery are influenced by industrial policies, quality standards, and safety frameworks.
Key policy and regulatory influences include:
-
Manufacturing promotion programs
Initiatives supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology encourage domestic electronics production and assembly capabilities. -
Quality and safety standards
Guidelines aligned with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) influence process control, documentation, and equipment usage. -
Electronics sector development policies
National programs promote infrastructure development for electronics manufacturing clusters. -
Environmental and workplace safety guidelines
Regulations guide safe handling of soldering materials, equipment operation, and waste management.
These frameworks aim to strengthen manufacturing capability while maintaining quality, safety, and environmental responsibility.
Tools and Resources Supporting Electronic Assembly Knowledge
A variety of technical tools and informational resources help learners and professionals understand electronic assembly machinery and manufacturing workflows.
Commonly referenced resources include:
-
PCB design and manufacturing software
Used to create layouts compatible with automated assembly processes. -
Production line simulation tools
Help visualize machine placement, throughput, and workflow balance. -
Process monitoring dashboards
Display real-time data from pick-and-place machines and soldering equipment. -
Technical standards documentation
Provide reference information on component placement, soldering profiles, and inspection criteria. -
Electronics manufacturing knowledge portals
Offer educational material on assembly techniques and equipment fundamentals.
These resources support better understanding of how electronic assembly machinery operates within a production environment.
Core Types of Electronic Assembly Machinery
| Machinery Type | Primary Function | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Pick-and-Place Machines | Component placement | SMT assembly lines |
| Solder Paste Printers | Apply solder paste | PCB preparation |
| Reflow Ovens | Melt solder joints | Surface-mount soldering |
| Wave Soldering Systems | Solder through-hole parts | Mixed-technology boards |
| AOI Systems | Visual inspection | Defect detection |
Typical Electronic Assembly Workflow
| Stage | Key Activity | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Printing | Solder paste application | Prepare PCB pads |
| Placement | Component positioning | Ensure accuracy |
| Soldering | Thermal processing | Create electrical joints |
| Inspection | Visual and optical checks | Identify defects |
| Testing | Functional verification | Confirm performance |
FAQs: Electronic Assembly Machinery and Manufacturing
What is electronic assembly machinery?
It refers to equipment used to place, solder, and inspect electronic components on circuit boards.
Why is surface-mount technology widely used?
SMT allows higher component density and supports compact electronic designs.
How does automated inspection improve manufacturing quality?
Inspection systems detect placement or soldering issues early, reducing defects in later stages.
Is electronic assembly machinery adaptable to different products?
Modern machinery is designed for flexibility, allowing adjustments for various PCB designs.
How does data integration help electronics manufacturing?
Process data supports traceability, quality analysis, and continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Electronic assembly machinery plays a central role in modern electronics manufacturing by enabling precise, repeatable, and scalable production of electronic components and systems. As electronics continue to become more compact and complex, the importance of advanced assembly equipment grows alongside them.
Recent developments highlight a trend toward intelligent, connected machinery that supports quality assurance and efficient workflows. In India, supportive industrial policies and international standards help guide the responsible use of electronic assembly machinery. Understanding these systems provides valuable insight into how everyday electronic products are manufactured and how industrial technology continues to evolve.